Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. It is one of the most common diseases in men. Mostly men over 30 are affected. If left untreated, the disease progresses rapidly and leads to serious complications – infertility, impotence and cancer.
Most often, prostatitis is manifested by painful urination, purulent and bloody discharge in the urine and sexual dysfunction.
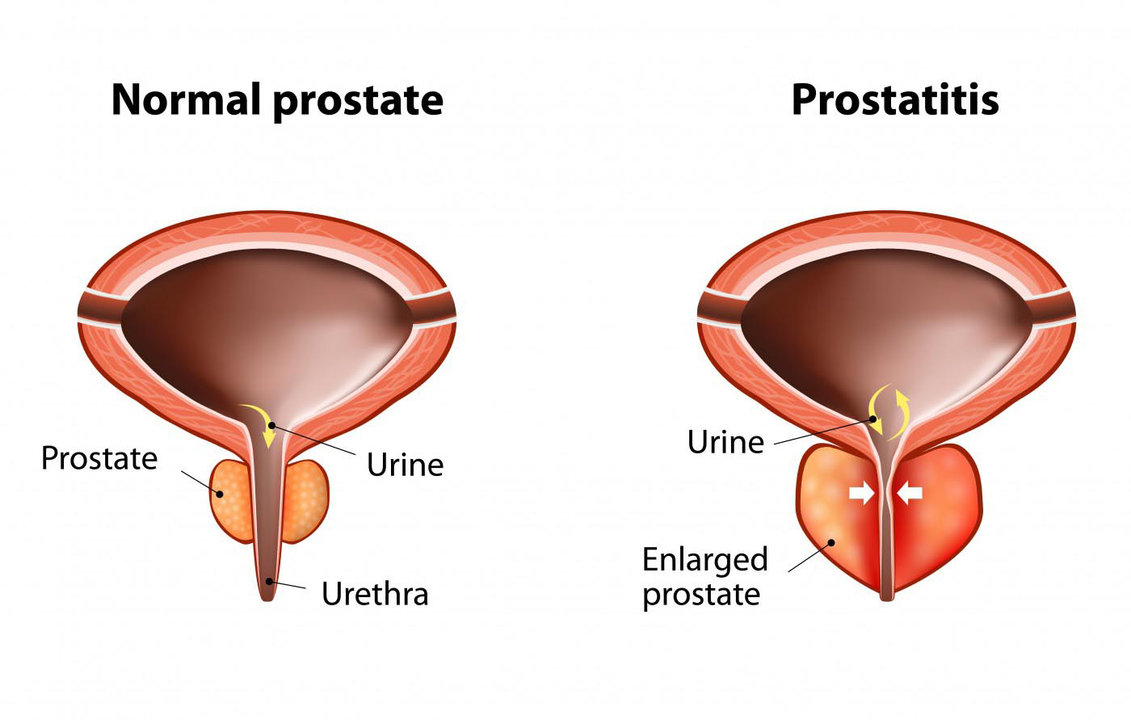
The prostate is the organ that produces sperm and regulates urination. It is located below the bladder. It consists of three departments. During ejaculation, the prostate gland begins to contract, pushing the seminal fluid through the urethra. The gland is involved in the limitation of urinary incontinence, in the formation of an erection and in the production of sperm.
Prostate juice contains a large amount of proteins, fats, enzymes and even some vitamins. The juice dilutes the seminal fluid, thus promoting sperm viability. The prostate gland is an active organ. It is dependent on hormonal levels and itself participates in the formation of sex hormones.
reasons
It is difficult to determine the exact reason that caused the development of prostatitis in a particular person. Most likely, it will be a complex of factors that to one degree or another led to the problem.
Let's look at the causes and factors that can contribute to the development of prostatitis:
- Hypothermia and stress. The body's defenses are reduced, which contributes to the appearance of inflammatory processes.
- Hormonal imbalance. The level of sex hormones affects the activity of the prostate gland.
- Sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections.
- Various disorders of the mechanisms in the body: urination disorders, congestion in the pelvis. A hypodynamic lifestyle and tight underwear interfere with blood circulation in the pelvis. And problems with urination contribute to irritation of the tissue of the gland and cause prostatitis. Constipation can also be considered a predisposing factor.
- Prolonged abstinence from intercourse, interrupted intercourse, or artificial prolongation of intercourse. This leads to enlargement of the gland and its inflammation.
- Poor nutrition and alcohol abuse.
Infection of the prostate gland can occur in 4 ways:
- Descending – enters with the flow of urine.
- Ascending - rises along the urethra.
- Lymphogenic - along with the flow of lymph.
- Hematogenous - along with the blood stream.
Symptoms and signs of prostatitis
Symptoms of prostatitis can be different. According to the nature of the course, prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic.
Common signs of prostatitis include the following:
- problems with urination - it is frequent, intermittent and difficult;
- deterioration of erection;
- burning sensation in groin;
- urine is cloudy and contains fibers;
- the orgasm is not bright;
- increased fatigue;
- reduced potency;
- depression, anxiety.
Acute prostatitis most often begins with an increase in body temperature to 39-40 degrees. The prostate gland swells, causing problems with urination. It is difficult and accompanied by pain.
During an exacerbation of prostatitis, the patient experiences pain in the perineum, as well as in the rectum, groin and sacrum.
Acute prostatitis can be catarrhal, follicular and parenchymal. Features of acute prostatitis:
- Follicular acute prostatitis is characterized by weak stream pressure during urination. It is accompanied by severe pain that can radiate to the anal area, especially intensifying during defecation. A slight rise in temperature is possible.
- Parenchymal acute prostatitis is characterized by unexpected pain with pulsation in the perineal area. Intoxication of the body is observed, the temperature can reach 40 degrees. It is often accompanied by urinary retention.
- Catarrhal acute prostatitis causes pain in the perineum, frequent urination and pain during urination.
Chronic prostatitis can develop from an acute form, but more often it immediately develops into a chronic form. Symptoms are erased, without clear signs and manifestations.
Symptoms and signs caused by chronic prostatitis:
- decreased erection and libido;
- reduced flow pressure during urination;
- spasms and pain when urinating;
- pains in the perineum, anus, sacrum.
Since the signs of chronic prostatitis are not clearly expressed, the patient often does not pay attention to the symptoms for a long time, which aggravates its development and can cause complications.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
Medicine does not stand still and diagnosing prostatitis is not difficult. After taking an anamnesis, the doctor can prescribe various diagnostic methods to confirm the diagnosis of prostatitis.
- Rectal palpation of the prostate to diagnose prostatitis. It will reveal pain and increased size, and these are characteristic signs of the inflammatory process in it, and during palpation, the secretion of the prostate gland is released, which is sent for analysis.
- Ultrasound examination.
- Microscopic examination of prostatic secretion.
- Bacteriological examination of urine.
- A smear of mucous membranes and glandular secretions for infection.
- Analysis of a smear from the urethra to determine sexually transmitted infections that can cause prostatitis.
- Blood test to determine sex hormones.
These diagnostic measures help not only to confirm the diagnosis, since the symptoms are generally quite pronounced, but also to identify the cause of the disease.
Treatment of prostatitis
Currently, there are many options for treating prostatitis. These include traditional methods and methods of folk medicine. Traditional medicine can serve as an adjunct to the main therapy. Self-treatment of prostatitis is dangerous, as it can lead to complications.
Doctors always resort to the traditional, medicinal method of treating prostatitis. This helps to relieve swelling, severe inflammation and normalize the functioning of the prostate gland.
A complex of different methods is usually prescribed:
- rectal suppositories. Reduce pain and relieve inflammation;
- injections;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- instillation - the drug is injected directly into the prostate;
- micro enemas;
- tableted medicines. Most often antibacterial drugs;
- alpha blockers.
The complex of therapeutic measures is selected individually depending on the degree of the disease, the manifestation of symptoms and the expected therapeutic effect for the patient.
If a bacterial cause of prostatitis is found, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which can destroy several strains of bacteria. They can be in the form of suppositories, in the form of tablets and in the form of injections.
Pain relievers are used to relieve pain.
Alpha-blockers - help to relax the muscles of the urethra, which is a consequence of prostatitis. Various muscle relaxants are used to relieve tension in the perineal area.
A necessary step would be to improve circulation to relieve congestion and take vitamins.
In the treatment of prostatitis, various physiotherapeutic procedures and prostate massage are mandatory. Prostate massage is used in all forms and stages of disease development, improves blood circulation and squeezes out secretions with a pathogenic environment in the urethra.
Some scientists are skeptical about this method of treating prostatitis, arguing that the pathogenic environment penetrates further into the genitourinary system and contributes to inflammation of other organs. Experiments are currently being conducted, this point of view has not been clinically disproved or proven, therefore, massage is an integral method of treating prostatitis.
Traditional treatment at home
Traditional medicine is often used in the treatment of prostatitis at home. If chronic prostatitis is diagnosed, additional therapy with folk remedies will be very useful. It will not be superfluous in case of an acute manifestation of prostatitis, but treatment only at home is unacceptable.
Among the popular methods, the following can be called quite effective:
- Treatment of prostatitis with pumpkin seeds. Pumpkin seeds contain a large amount of zinc, which men need regardless of whether they have prostatitis.
- Treatment of prostatitis with parsley - helps relieve inflammation and normalize sexual function. Contains a large amount of vitamins.
- Treatment of prostatitis with infusions of hemlock and celandine. This method should be used with caution, as these herbs are poisonous and strict adherence to dosage and dosing regimen is required.
- Treatment of prostatitis with wormwood. It is used to relieve inflammation and remove purulent infection.
- Treatment of prostatitis with garlic, fennel, hazelnuts, chestnuts, propolis, herbs, etc.
Most of these methods are aimed at relieving inflammatory processes and normalizing sexual function. A large number of different vitamins saturate the body, which plays a role in preventing exacerbation of prostatitis.
Consequences of prostatitis
If you refuse and the treatment of prostatitis is not started in a timely manner, there is a high probability of developing serious complications. Among the complications:
- infertility;
- impotence;
- DHP;
- prostate cancer and others.
If treatment is refused, the infection will further penetrate into nearby tissues. Other prostate conditions can also develop, including stones and cysts.
With prostatitis, the level of sex hormones decreases, which leads to a decrease in sexual desire (libido). Erectile dysfunction begins and premature ejaculation may occur. Impotence is possible.
Prostatitis also leads to infertility. This problem is especially common in those patients who have developed chronic prostatitis. This complication occurred in half of these patients.
Sclerosis of the prostate gland may develop. In this case, the gland partially or completely stops functioning. This problem is accompanied by severe pain, sexual dysfunction and problems with urination.
Prostate adenoma and prostate cancer are the most dangerous complications of prostatitis.
The problems and complications that prostatitis leads to affect a man's sex life in one way or another. This leads to psychological problems, stress and depression.
It is important to carefully monitor the signs in order to recognize chronic prostatitis in time.
Prevention of prostatitis
Prevention of exacerbations is aimed at health monitoring and timely identification of problems. Since in most cases prostatitis is a consequence of untreated diseases of the genitourinary system, special attention should be paid to the treatment of such diseases.
Prostatitis is considered a disease that is easier to prevent than to treat.
Of the preventive methods, the most important are:
- Sports activities. They serve to improve blood circulation in the pelvis, prevent congestion and strengthen the pelvic muscles.
- Regular sex life. Medicines for artificial prolongation of intercourse, interruption of intercourse and suppression of ejaculation are undesirable.
- Renunciation of promiscuity. Violent sex life leads to sexually transmitted infections.
- Proper, healthy eating.
- Refusal of alcohol.
- Strengthening the body's defenses, avoiding hypothermia.
- Minimize stress.
Prostatitis has a low rate of self-treatment or home treatment. Therefore, at the first signs, you should immediately contact a urologist to prescribe adequate treatment. You should also carefully monitor the signs that indicate chronic prostatitis and consult a doctor in time.































